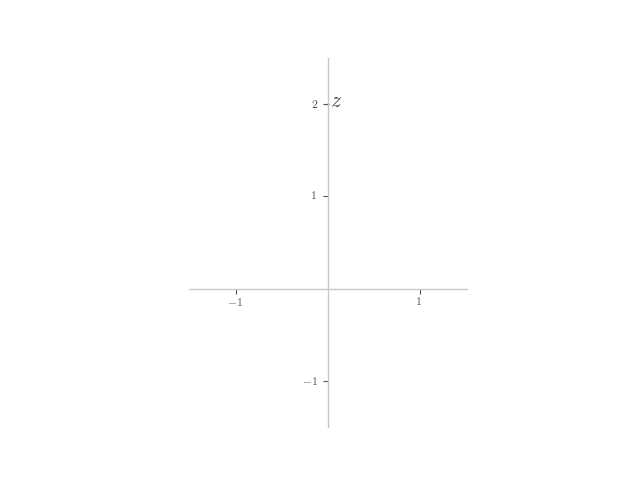
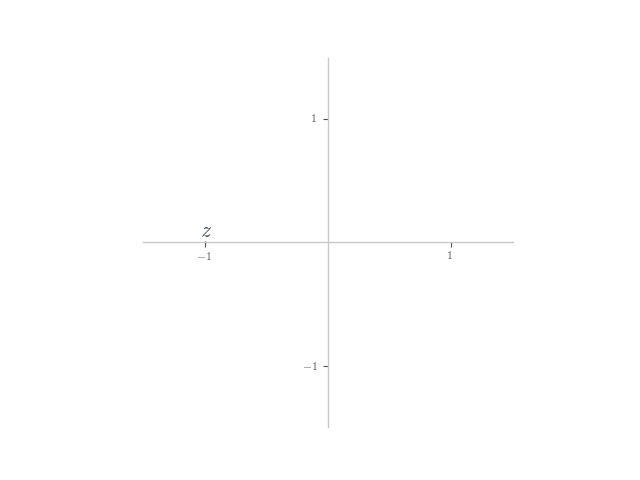
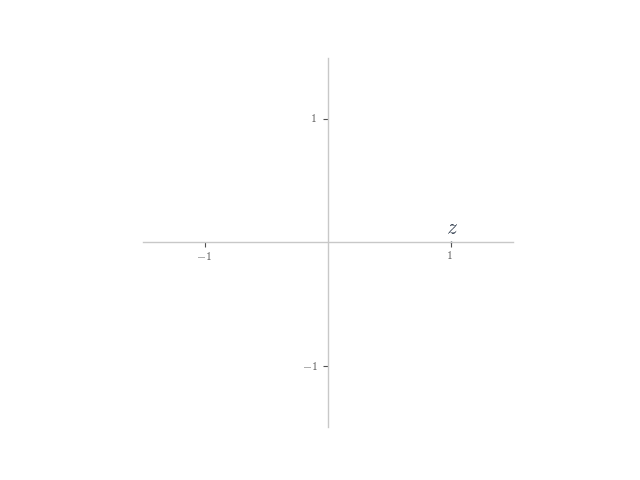
Addition and subtraction
Exercises
Problem set
Find the values of the following.
Problem set
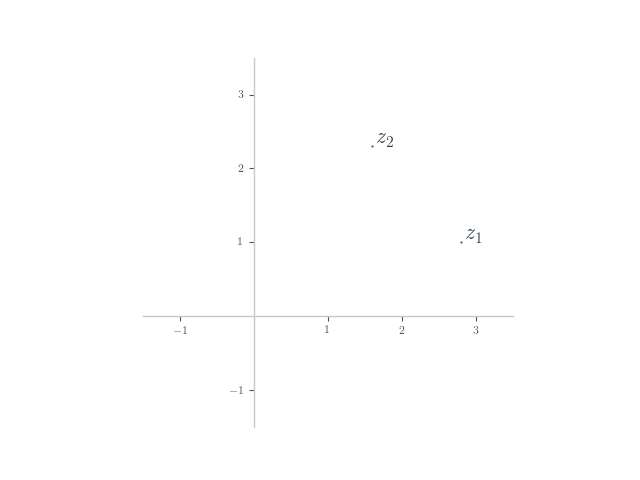
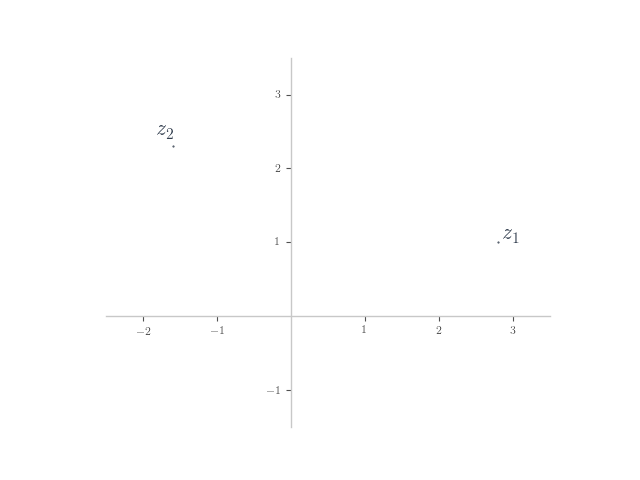
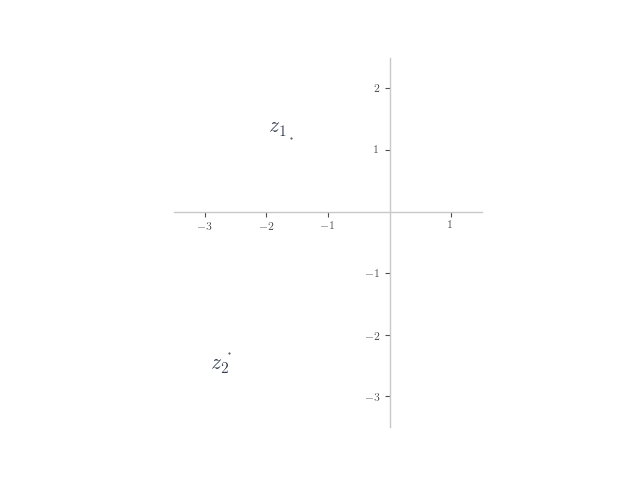
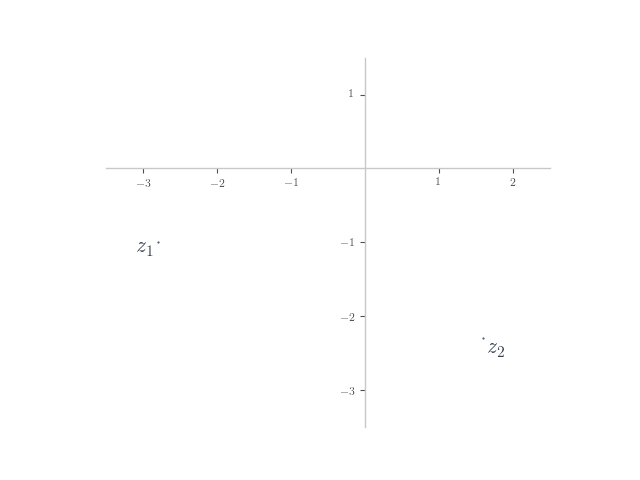
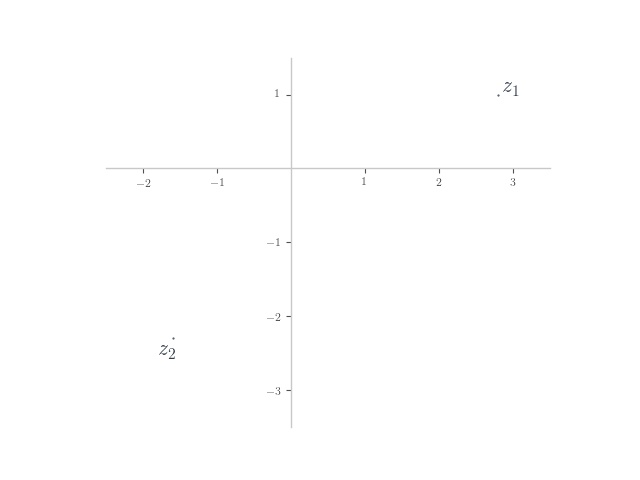
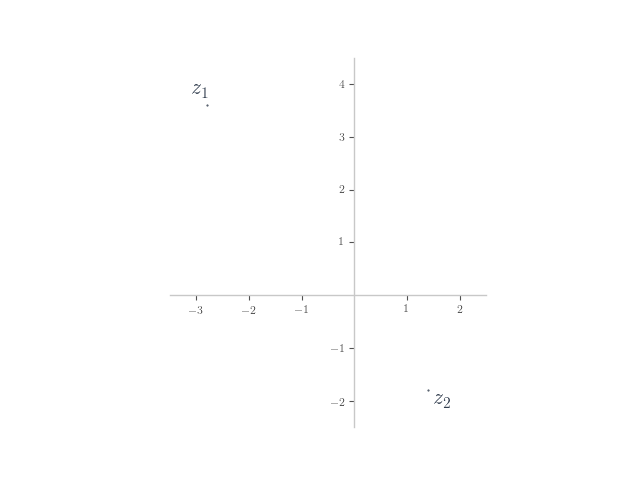
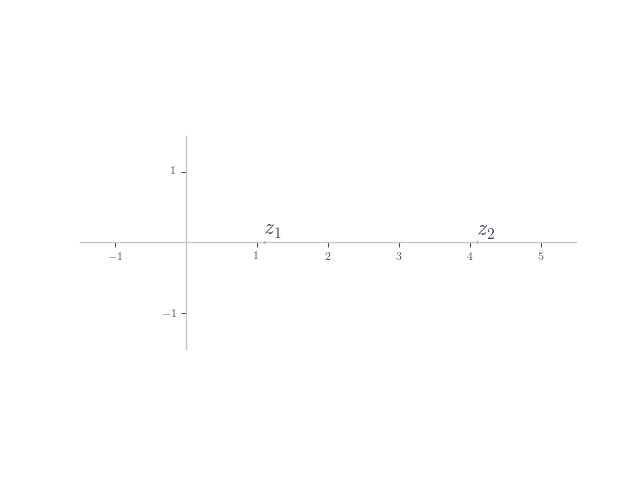
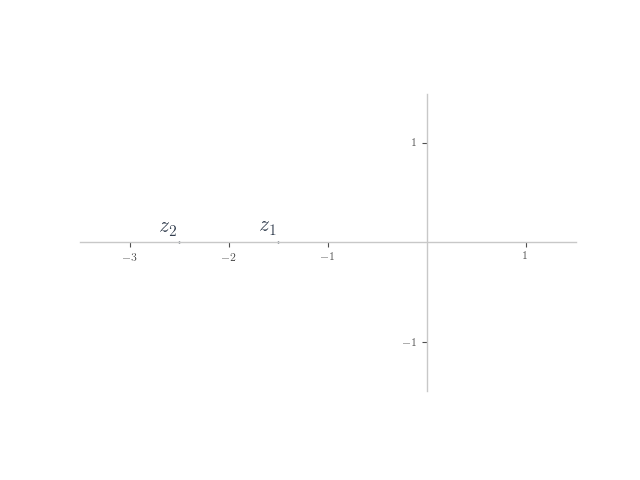
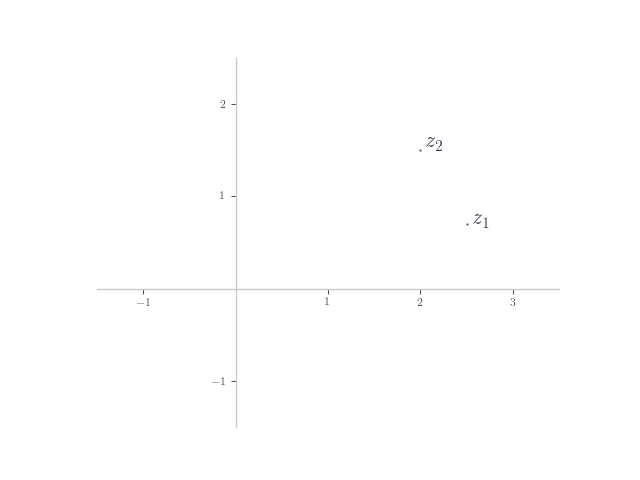
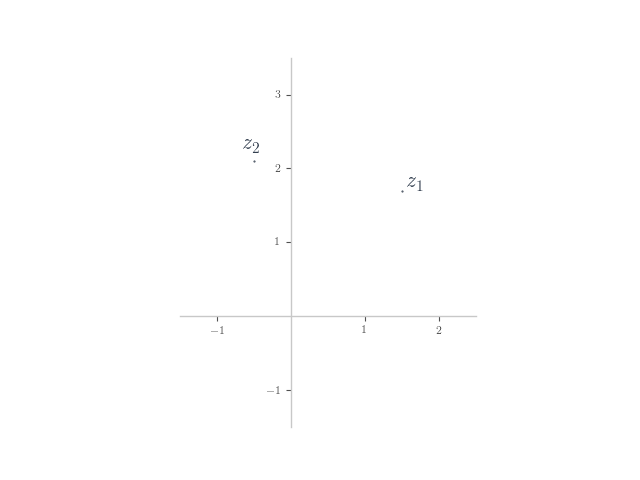
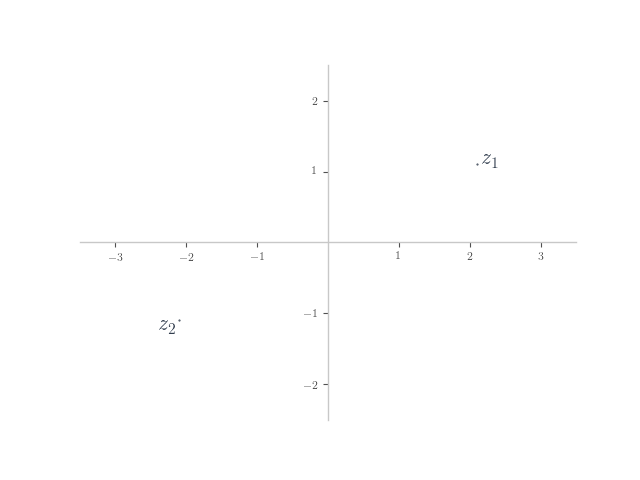
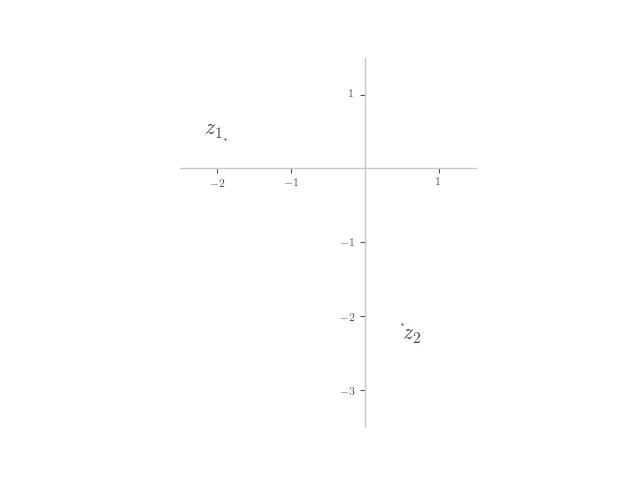
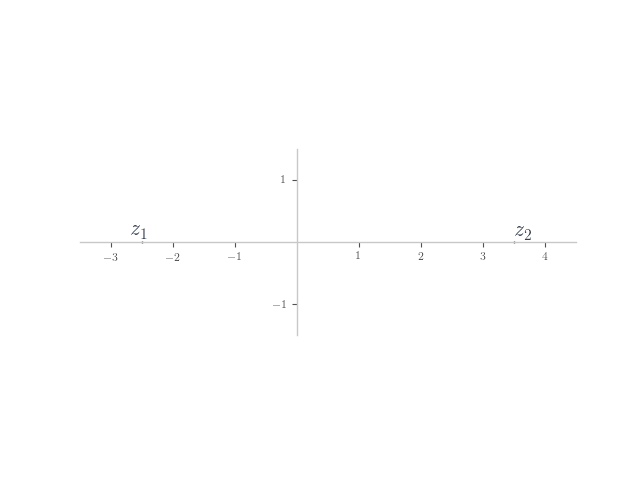
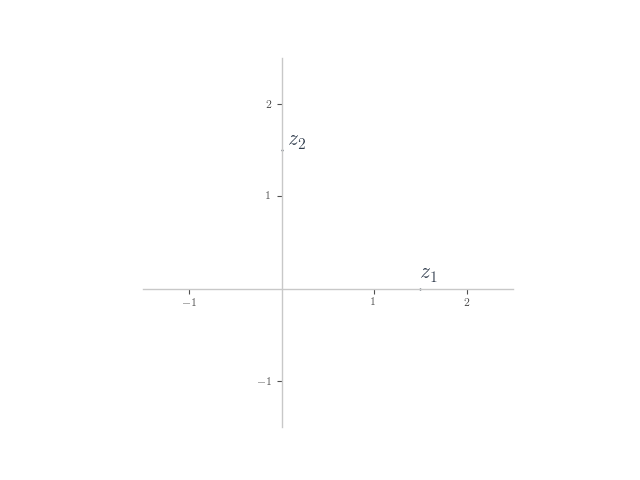
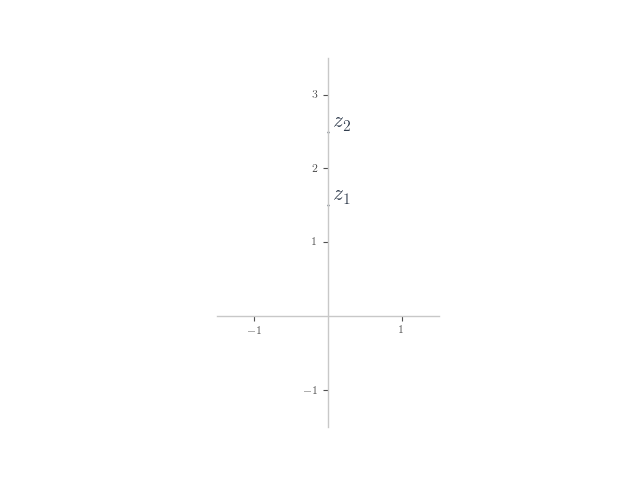
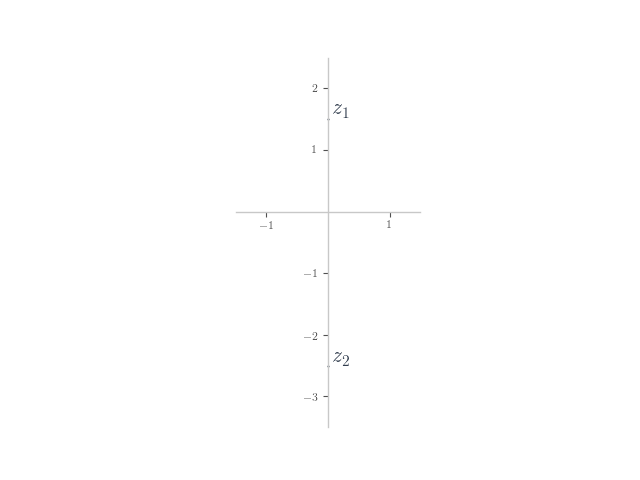
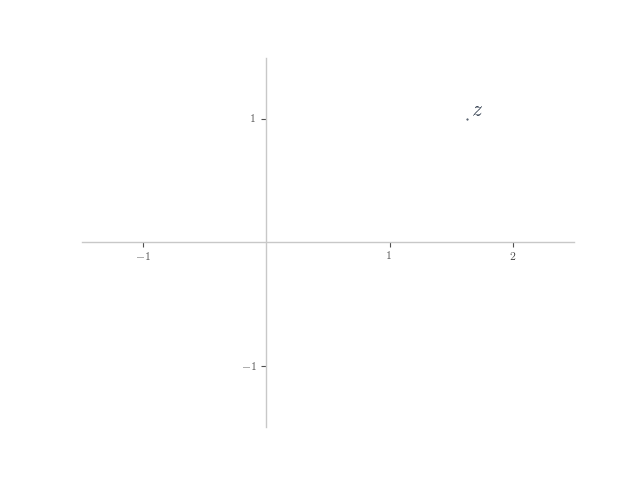
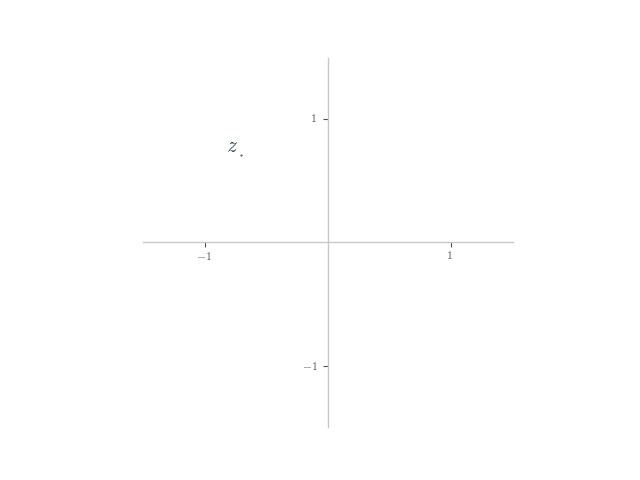
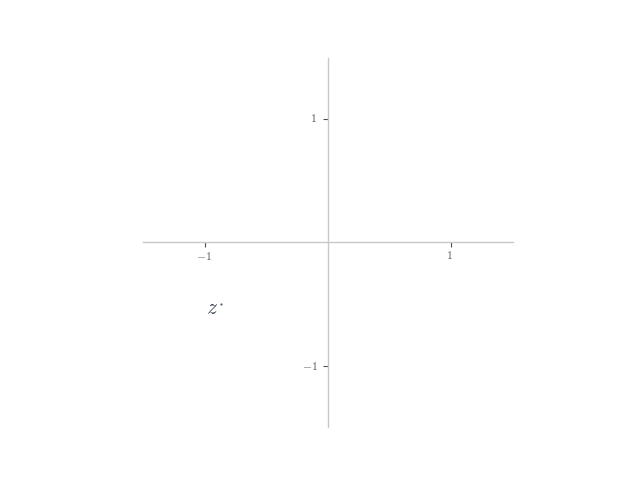
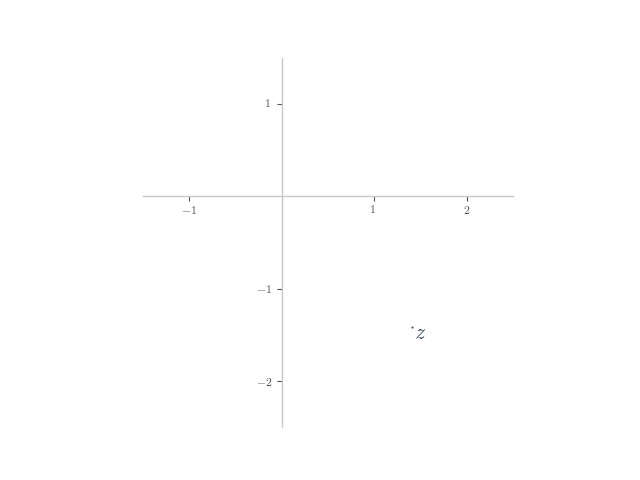
In each of the following, planar numbers and
are shown on the Argand plane. Plot the planar number
on the plane.
Modulus and argument
Exercises
Problem set
For each of following planar numbers, mark the number on the Argand plane and find the modulus of the number.
Problem set
For each of following planar numbers, mark the number on the Argand plane and find the argument of the number.
Problem set
In each of the following problems, find the Cartesian coordinates of the planar number .
Problem set
In each of the following problems, find the Cartesian coordinates of the planar number .
Problem set
In each of the following problems, find the Cartesian coordinates of the planar number .
Polar form
Exercises
Problem set
Write each of the following planar numbers in polar form.
Problem set
Write each of the following planar numbers in polar form.
Problem set
Write each of the following planar numbers in polar form.
Multiplication
Exercises
Problem set
Evaluate the following.
Problem set
Evaluate the following.
Problem set
In each of the following, planar numbers and
are shown on the Argand plane. Plot the planar number
on the plane.
Problem set
In each of the following, planar numbers and
are shown on the Argand plane. Plot the planar number
on the plane.
Conjugate
Exercises
Problem set
For each of the following problems, find the conjugate of the given planar number.
Problem set
For each of the following problems, find the conjugate of the given planar number, and express your answer in polar form.
Problem set
For each of the following problems, plot the conjugate of the given planar number.
Problem set
In each of the following problems, solve for .
Division
Exercises
Problem set
Evaluate the following.
Problem set
Find the values of each of the following.
Exponentiation
Exercises
Problem set
Evaluate the following.
Problem set
In the each of the following, the planar number is defined in terms of the planar number
, and the number
is shown on the Argand plane. Plot the number
on the plane.
Roots
Exercises
Problem set
In the each of the following, the planar number is defined in terms of the planar number
, and the number
is shown on the Argand plane. Plot the planar numbers that
could be equal to, on the plane.
Problem set
Find all the possible values of the following.
Problem set
Find all the possible values of the following.
Complex numbers
Exercises
Problem set
- Who originated planar numbers and when?
Problem set
Evaluate the following.
Problem set
Evaluate the following.
Problem set
For each of the following, if the complex number is given in polar form, convert it into rectangular form, and if the complex number is given in rectangular form, convert it into polar form.
Problem set
Evaluate the following.
Problem set
Evaluate the following.
Problem set
Evaluate the following.
Problem set
In each of the following problems, one or more of the complex numbers ,
and
are shown on the complex plane. And, a complex number
is defined in terms of the complex numbers shown. Plot
on the complex plane.
Problem set
For complex numbers and
, justify the following.
Miscellaneous
Exercises
Problem set
Following are the notations used for this problem set:
-
– Set of Natural numbers
-
– Set of Rational numbers
-
– Set of Integers
-
– Set of Whole numbers
-
– Set of Real numbers
-
– Set of Complex numbers
- If
denotes the set of purely imaginary numbers, which of the following is/are true:
,
,
?
- If
denotes the set of irrational numbers, which of the following is/are true:
,
,
,
?
- If
denotes the set of purely imaginary numbers, which of the following is true:
,
?
- Is this true or false:
?
- Fill in the missing sets in the set inclusion hierarchy:
.
Problem set
- Plot the function
. What are the zeroes of this function?
- Plot the function
. What are the zeroes of this function?
- Plot the function
. What are the zeroes of this function?
Problem set
Express the following in the form of , where
and
are real numbers.
- For a complex number
,
. What is the value of
?
- In general for two complex numbers
and
, triangle inequality
holds.
- What happens when
?
- What happens when
?
- What happens when
-
and
. Evaluate
such that
.
-
. Determine
such that
.